Elevating Recovery: The Transformative Power of Exercise on Mental Health
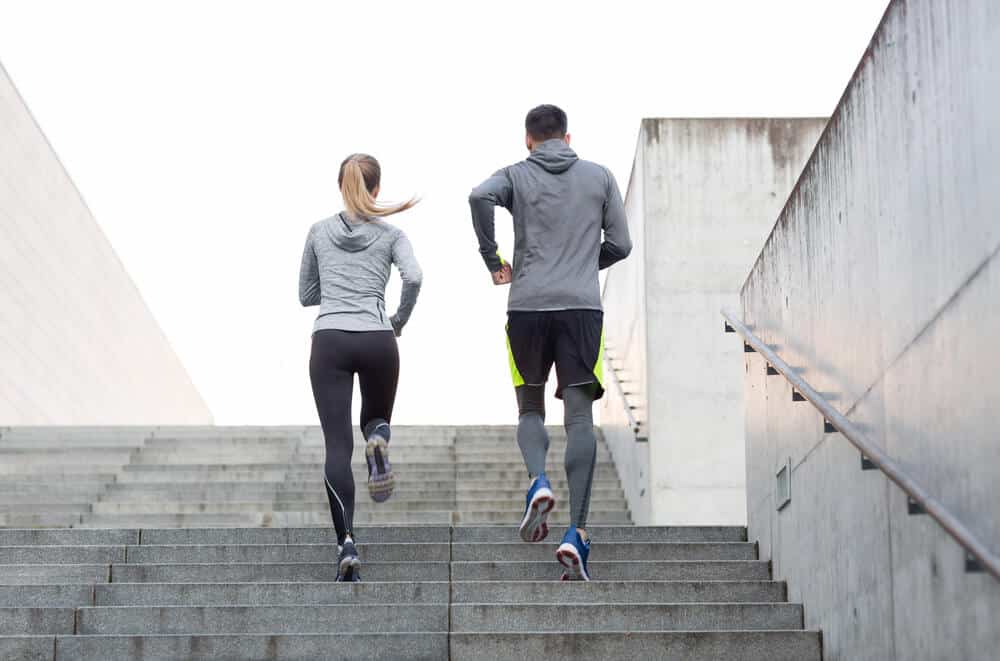

Embarking on the journey of recovery is a profound and courageous endeavor that encompasses healing the mind, body, and spirit. While therapy and support networks play crucial roles, the impact of exercise on mental health during recovery is a dynamic and transformative force. In this exploration, we delve into the profound connection between physical activity and mental well-being, shedding light on how incorporating exercise into the recovery process can bring about positive and enduring change.
Understanding the Mind-Body Connection:
- Release of Endorphins:
- Exercise triggers the release of endorphins, often referred to as “feel-good” neurotransmitters. These chemicals interact with receptors in the brain, reducing the perception of pain and promoting a sense of well-being. The endorphin boost from exercise can contribute to improved mood and reduced stress levels.
- Reduction of Stress Hormones:
- Physical activity helps regulate the body’s stress response by reducing the levels of stress hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline. Regular exercise provides a healthy outlet for stress, preventing the accumulation of tension that can contribute to anxiety and depressive symptoms.
- Enhancement of Neurotransmitters:
- Exercise positively influences neurotransmitters, including serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters play key roles in mood regulation, pleasure, and motivation. By promoting a healthy balance of neurotransmitters, exercise contributes to emotional stability.
The Impact of Exercise on Mental Health in Recovery:
- Mood Regulation and Stability:
- Individuals in recovery often experience fluctuations in mood as they navigate the challenges of abstaining from substances. Exercise acts as a natural mood regulator, fostering stability and reducing the intensity of mood swings. Regular physical activity can contribute to a more positive and balanced emotional state.
- Coping with Cravings and Triggers:
- Exercise provides a constructive and healthy means of coping with cravings and triggers associated with addiction. Engaging in physical activity redirects attention and energy toward a positive outlet, diminishing the allure of substance use as a coping mechanism.
- Boosting Self-Esteem and Confidence:
- Recovery is a journey of self-discovery and empowerment. Regular exercise contributes to improvements in physical fitness and body image, boosting self-esteem and confidence. This positive self-perception can be instrumental in fostering a resilient mindset during the recovery process.
- Improved Sleep Quality:
- Sleep plays a vital role in mental health and overall well-being. Exercise has been linked to improved sleep quality, aiding individuals in recovery who may face challenges related to sleep disturbances. Quality rest supports emotional regulation and cognitive function.
- Stress Reduction and Anxiety Management:
- Physical activity serves as a powerful tool for stress reduction and anxiety management. Engaging in exercise helps dissipate accumulated tension, promotes relaxation, and provides a healthy outlet for anxious energy. This, in turn, contributes to a calmer and more centered mental state.
Practical Tips for Incorporating Exercise into Recovery:
- Start Small and Gradual:
- Begin with manageable and achievable exercise goals, especially if you are new to regular physical activity. Starting small and gradually increasing intensity and duration helps build a sustainable exercise routine.
- Choose Enjoyable Activities:
- Opt for activities that you find enjoyable and fulfilling. Whether it’s jogging, swimming, yoga, or team sports, engaging in activities that bring you joy increases the likelihood of maintaining a consistent exercise routine.
- Mix Cardiovascular and Strength Training:
- Incorporate a combination of cardiovascular and strength training exercises. Cardiovascular activities, such as walking or cycling, improve heart health and boost endorphin release. Strength training enhances muscle tone and overall physical well-being.
- Explore Mind-Body Practices:
- Mind-body practices, such as yoga and tai chi, offer holistic benefits for mental and physical health. These practices emphasize the connection between body and mind, promoting relaxation, mindfulness, and flexibility.
- Connect with Others:
- Exercise can be a social activity that fosters connections with others. Joining group classes, sports leagues, or fitness communities provides a supportive environment and contributes to a sense of belonging.
Seeking Professional Guidance:
- Consultation with Healthcare Providers:
- Before initiating an exercise routine, individuals in recovery are advised to consult with their healthcare providers. This is particularly important if there are pre-existing health conditions or concerns that may influence the type and intensity of exercise recommended.
- Incorporating Exercise into Treatment Plans:
- Treatment plans for addiction recovery can integrate exercise as a therapeutic component. Some treatment centers offer structured physical activity programs tailored to the unique needs and preferences of individuals in recovery.
Exercise stands as a potent ally in the journey of recovery, offering a myriad of mental health benefits that complement therapeutic interventions and support networks. By recognizing the transformative power of physical activity in regulating mood, managing stress, and fostering overall well-being, individuals in recovery can empower themselves to embrace a holistic approach to healing. Incorporating exercise into the recovery process is not just about fitness; it’s a dynamic pathway toward resilience, self-discovery, and enduring mental health.